When it comes to car engine codes, deciphering them accurately is essential for timely troubleshooting. Among the various codes that can leave car owners and mechanics scratching their heads, “fuel SYS 1 CL” often falls into the tricky category.
To understand this code, let’s break it down.
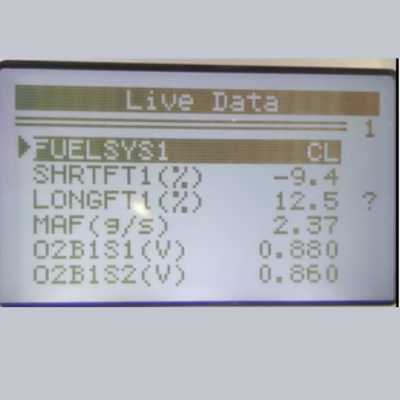
The “fuel SYS” refers to the fuel system, an integral part of any vehicle’s operation. The number “1” denotes bank 1 of the fuel injector, which supplies fuel to a specific set of cylinders in the engine and “CL” stands for closed loop, indicating that the fuel system operates within a specified range of parameters.
It’s worth noting that the terms “fuel SYS 1 CL” and “fuel SYS 2 CL” are commonly used by generic scanners to indicate the left or right bank of the engine. This distinction helps pinpoint the location of potential issues when diagnosing problems.
In this comprehensive blog post, we aim to serve as your ultimate guide to understanding fuel SYS 1 CL, its underlying causes, and practical solutions to address it.
Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a mechanic, or simply seeking knowledge on engine codes, this post will equip you with the necessary insights to navigate and resolve fuel system challenges effectively.
What Does Fuel SYS 1 CL Mean?
The “Fuel Sys 1 CL” message indicates that the fuel system on bank 1 is operating in closed-loop mode. Closed loop mode signifies that the engine utilizes the oxygen sensor to regulate fuel injection quantity precisely.
In this mode, the engine constantly monitors the feedback from the oxygen sensor to fine-tune the fuel-to-air ratio, ensuring optimal combustion efficiency.
The closed-loop system enables the engine to make real-time adjustments to maintain the ideal fuel mixture for improved performance and reduced emissions.
In closed-loop mode, the engine control unit (ECU) utilizes the input from the lambda sensor in the exhaust to accurately determine the appropriate amount of fuel to inject into the engine.
The ECU can dynamically adjust the air/fuel ratio based on real-time combustion feedback. When the lambda sensor detects a rich mixture, the ECU reduces the fuel injection quantity.
When the mixture is too lean, the ECU increases the fuel injection to achieve optimal combustion.
In this mode, the engine control unit (ECU) relies heavily on the oxygen sensor to determine the ideal amount of fuel to inject into the system.
Common Causes of Fuel SYS 1 CL code
- A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate readings, leading to the “Fuel SYS 1 CL” code.
- If they become clogged or dirty, they may not deliver the proper amount of fuel, causing the engine to operate outside the closed loop mode.
- Any leaks in the vacuum system, such as cracked hoses or intake manifold gasket issues, can result in incorrect air/fuel mixture readings, triggering the error code.
- A defective MAF sensor can disrupt the proper calculation of air intake, causing the engine to run outside the closed loop mode.
- Insufficient or excessive fuel pressure can affect fuel delivery, leading to an incorrect air/fuel mixture and triggering the code.
- Leaks or damage in the exhaust system, including the catalytic converter, can impact the oxygen sensor readings and cause the code to appear.
- Malfunctions or software glitches in the ECU can disrupt the closed-loop control system, resulting in the “Fuel SYS 1 CL” code.
How To Fix Fuel SYS 1 CL?
1) Check and replace the oxygen sensor
Inspect the oxygen sensor for any damage or wear. If necessary, replace it with a new sensor to ensure accurate readings and proper functioning of the closed-loop system.
2) Clean or replace fuel injectors
Use a suitable fuel injector cleaner if they are clogged or dirty. In severe cases, it may be necessary to replace the injectors to restore proper fuel delivery.
3) Inspect and repair vacuum leaks
Thoroughly examine the system for leaks. Repair or replace damaged hoses, gaskets, or other components to eliminate vacuum leaks affecting the air/fuel mixture.
4) Check and replace the mass air flow sensor (MAF)
If the MAF sensor is faulty, consider replacing it to ensure accurate measurement of an air intake, which is crucial for maintaining the closed loop operation.
5) Verify and adjust fuel pressure
Check the fuel pressure using a fuel pressure gauge. If it’s outside the specified range, address the issue by repairing or replacing the fuel pressure regulator or other related components.
6) Repair exhaust system problems
Inspect the exhaust system, including the catalytic converter, for leaks or damage. Fixing or replacing damaged components will help maintain proper oxygen sensor readings.
7) Perform an ECU reset or update
If the engine control unit (ECU) is suspected to be the cause, reset the ECU by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes. Alternatively, consult a professional to update or reprogram the ECU if necessary.
You May Also Like To Read:
Affiliate Disclosure: Cars Escort is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases made through affiliate links on our site. Read Our Disclaimer .

