In 85% of situations, when the check engine light flashes and then stops, it usually indicates a minor engine issue, such as loose wires, bad oxygen sensors, a loose fuel cap, or a faulty mass airflow sensor. However, in 15% of cases, the flashing check engine light may indicate more severe problems such as engine misfire and malfunctioning catalytic converter.
The check engine light also known as malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and CEL is a common concern for many vehicle owners. It is an important indicator that something might be amiss within the intricate system of your car.
So, what does it mean when the CEL suddenly starts blinking and then stops when driving?
This peculiar behavior can be puzzling and problematic, leaving car owners wondering whether they should panic or carry on as usual.
Understanding this enigmatic signal is crucial to take appropriate action and ensuring your beloved automobile’s longevity.
Why Check Engine Light Is Considered An Alarming Sign?
The Check Engine light is considered an alarming sign in vehicles because it indicates that there may be a problem with the vehicle’s engine or emission control system.
When the CEL appears on the dashboard, it is a warning from the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD) that something is malfunctioning.
Several reasons can cause the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) may come on, ranging from minor issues to more severe problems.
Ignoring the indicator can have consequences. The light is designed to alert the driver that a potential problem needs attention.
Ignoring it risks further damage to the vehicle or increased emissions, which can lead to more costly repairs in the long run.
In some regions, a vehicle with an illuminated Check Engine light may not pass emissions tests or inspections.
Why Check Engine Light Flashing Then Stops?
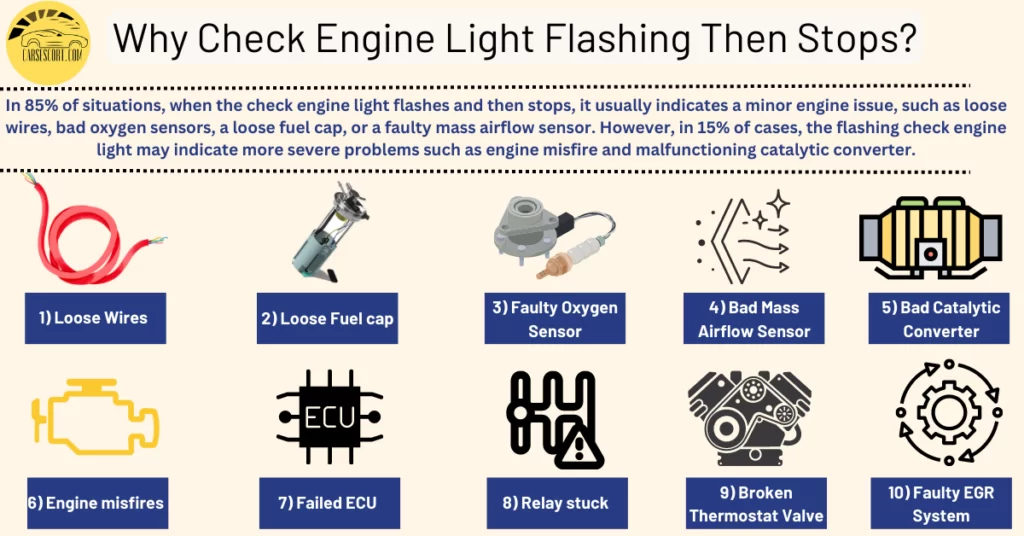
1) Loose or damaged electrical connections
Loose or damaged electrical connections in the engine can significantly impact the sensors’ proper functioning leads to blinking check engine light.
These sensors are crucial in monitoring the engine’s performance and relaying important information to the vehicle’s onboard computer system.
When the electrical connections become loose or damaged, the flow of electrical signals can be interrupted or distorted.
This disruption affects the accuracy and reliability of the sensor readings. As a result, the check engine light may start flashing as a warning to the driver that there is a problem with the engine.
2) Fuel cap is loose or not securely fastened
The fuel cap plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the fuel system by sealing the fuel tank. When the fuel cap is loose or not securely fastened, it allows air to enter the fuel system, disrupting the pressure balance within the system.
Modern vehicles are equipped with an evaporative emission control system, preventing harmful fuel vapors from being released into the atmosphere. This system relies on maintaining a sealed environment within the fuel system to capture and store these vapors.
When a vacuum leak occurs due to a loose gas cap, the evaporative emission control system detects abnormal pressure changes and triggers the flashing engine light and then stops while driving.
This warning light will notify the driver of a potential problem with the fuel system that requires attention.
3) Oxygen sensor becomes faulty or starts to deteriorate
The oxygen, or the O2 sensor, is vital to the vehicle’s emissions control system. It is located in the exhaust system and measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases.
This information is relayed to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the fuel injection system to maintain the ideal air-to-fuel ratio.
Faulty oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate readings or fail to provide any readings. As a result, the engine control unit cannot accurately adjust the fuel injection system, leading to an improper fuel-to-air ratio, and the blinking check engine light may start flashing.
Imbalance due to faulty oxygen sensor can result in inefficient combustion, decreased fuel economy, and increased emissions.
4) Bad mass airflow sensor
The mass airflow sensor (MAF) is a vital component of the engine management system. It measures the volume and density of the air entering the engine.
This information is used by ECU to determine the optimal fuel-to-air mixture for efficient combustion.
When the MAF sensor malfunctions, it can produce inaccurate readings or fail to provide them. As a result, the engine control unit cannot accurately calculate the required amount of fuel to be injected into the engine cylinders.
This can lead to a rich (excess fuel) or lean (insufficient fuel) fuel mixture, negatively impacting performance.
A bad airflow sensor can have several noticeable effects on the vehicle. One common consequence is reduced engine power and acceleration.
The engine may struggle to respond promptly and smoothly to driver inputs, resulting in sluggish performance.
The engine may idle roughly or experience intermittent stalling due to inaccurate airflow readings. The vehicle may sometimes experience hesitation or surge during acceleration, as the improper fuel-to-air ratio affects combustion efficiency.
When a lousy airflow sensor is detected, the ECU activates the check engine light flashing to warn the driver and then stops while driving.
The flashing check engine light indicates a more severe issue that requires immediate attention. Ignoring the problem can lead to further damage and increased repair costs.
5) Bad or malfunctioning catalytic converter
The catalytic converter’s primary function is to convert harmful pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and unburned hydrocarbons, into less harmful substances through chemical reactions. This process significantly reduces the environmental impact of the vehicle’s exhaust emissions.
A bad catalytic converter is activating the blinking check engine light. The onboard diagnostic system detects the issue and triggers the warning light to alert the driver that there is a problem with the catalytic converter or the emissions control system.
When a catalytic converter malfunctions or fails, it can negatively affect engine performance in several ways.
One noticeable effect is a decrease in power and responsiveness. The engine may feel sluggish and struggle to accelerate as the restricted flow of exhaust gases hampers its efficiency.
6) Engine misfires (Codes P0300-P0305)
An engine misfire is a significant problem that affects a vehicle’s smooth operation and performance. During normal combustion, each cylinder in the engine receives a spark from the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture and generating power.
However, when an engine misfires, this process is disrupted, resulting in a lack of power delivery and an unsteady operation and trigger the flashing check engine lights and P0300-P0305 trouble code.
Several potential causes can contribute to engine misfires. One common culprit is faulty spark plugs. Over time, spark plugs can become worn or fouled, leading to weak or inconsistent sparks.
This hinders proper ignition and can cause misfires. Similarly, damaged or deteriorated ignition coils, which generate high-voltage electricity to power the spark plugs, can also result in misfires.
Another possible cause is faulty fuel injector. Fuel injectors are responsible for precisely spraying fuel into the combustion chambers.
If they become clogged, dirty, or fail to operate correctly, the fuel distribution becomes irregular, leading to incomplete combustion and misfires.
Engine misfires can manifest various symptoms, including rough idling, noticeable shaking or vibrations, loss of power, or even hesitation during acceleration.
7) Failed engine control unit (ECU)
The engine control unit (ECU) is a sophisticated electronic module that acts as the brain of the engine, monitoring and controlling various aspects of its operation. It receives data from sensors throughout the vehicle, processes the information, and optimizes engine performance, fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other vital parameters.
When the ECU experiences a malfunction or fails, it can significantly affect the engine’s operation. One of the most noticeable indications is the flashing of the check engine light.
Unlike a steady check engine light, which may signify a less severe issue, a flashing check engine light indicates a critical problem that requires immediate attention.
A failed ECU can result in various symptoms that affect the engine’s performance and overall functionality. These may include erratic engine behavior, rough idling, stalling, loss of power, or even fails to start.
Other systems dependent on the ECU, such as the transmission or emissions control system, may also be affected.
8) Relay stuck or damaged air filter valve
The air filter valve relay is an electrical component that controls the operation of the air filter valve. The air filter valve regulates the engine’s air entering, ensuring the proper balance of fuel and air for combustion.
When the relay malfunctions or gets damaged, it can cause the air filter valve to become stuck in an incorrect position, obstructing or restricting the airflow to the engine and you may notice check engine light coming.
The disruption of proper airflow has several adverse effects on engine performance. Insufficient air supply can lead to an imbalance in the fuel-to-air ratio, causing inefficient combustion.
This can result in decreased power output, reduced fuel efficiency, and even engine misfires.
A stuck or damaged air filter valve relay can manifest in various symptoms. One of the most common indications is a flashing engine light.
The engine control unit (ECU) detects the disruption in the airflow and registers it as a critical issue, prompting the activation of the check engine light.
Other noticeable effects may include rough idling, engine hesitation or stumbling during acceleration, and decreased overall performance.
The vehicle may also experience a decrease in fuel efficiency, requiring more fuel to compensate for the restricted airflow.
9) Broken Thermostat Valve
The thermostat valve is a crucial component of the engine’s cooling system. Its primary function is to regulate the flow of coolant through the engine based on its temperature.
The thermostat valve remains closed when the engine is cold, preventing coolant from circulating. As the engine warms up, the thermostat valve gradually opens, allowing coolant to flow and maintain the its optimal operating temperature.
If the thermostat valve breaks or fails, it can seriously affect the engine’s temperature regulation. One of the most significant issues is engine overheating.
Coolant cannot circulate through the engine effectively when the thermostat valve fails to open properly or gets stuck in the closed position. As a result, heat builds up, and the engine’s temperature rises beyond the safe operating range.
Overheating can lead to engine components damage if not addressed promptly. It can cause warped cylinder heads, blown head gaskets, or shaking.
To prevent further damage and ensure safe operation, the engine control unit (ECU) activates the light when it detects the engine temperature exceeding normal limits.
10) Faulty EGR System
The EGR system redirects some of the exhaust gases rich in nitrogen oxides into the engine’s intake manifold. This process lowers the combustion temperature and reduces the formation of harmful nitrogen oxide emissions.
Several issues can arise when the EGR system malfunctions or its components fail, affecting engine performance and emissions.
One common problem is a faulty EGR valve. The EGR valve regulates the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. If the valve gets stuck in an open or closed position, it can disrupt the proper recirculation of exhaust gases, leading to performance issues.
A malfunctioning EGR system can cause various symptoms that affect engine operation. These may include rough idling, hesitation or stumbling during acceleration, reduced power output, and increased fuel consumption. A faulty EGR system can also result in increased emissions, potentially causing the vehicle to fail emissions tests.

You May Also Like To Read From Our Cars Guide:
Why Does The Check Engine Light Flashes And Turns Into A Solid Light?
When the check engine light starts flashing and then remains solid, it is often a telltale sign of an intermittent problem with a component on the verge of failure but occasionally manages to rectify itself temporarily.
Interestingly, even if the engine continues functioning without apparent issues, the check engine flashing light stays illuminated until the error code is effectively erased from the electronic control unit (ECU) memory.
However, should you reset the error code only to have the check engine light reappear, it becomes crucial to delve deeper into the matter to prevent potential damage.
What To Do If The Check Engine Light Flashes?
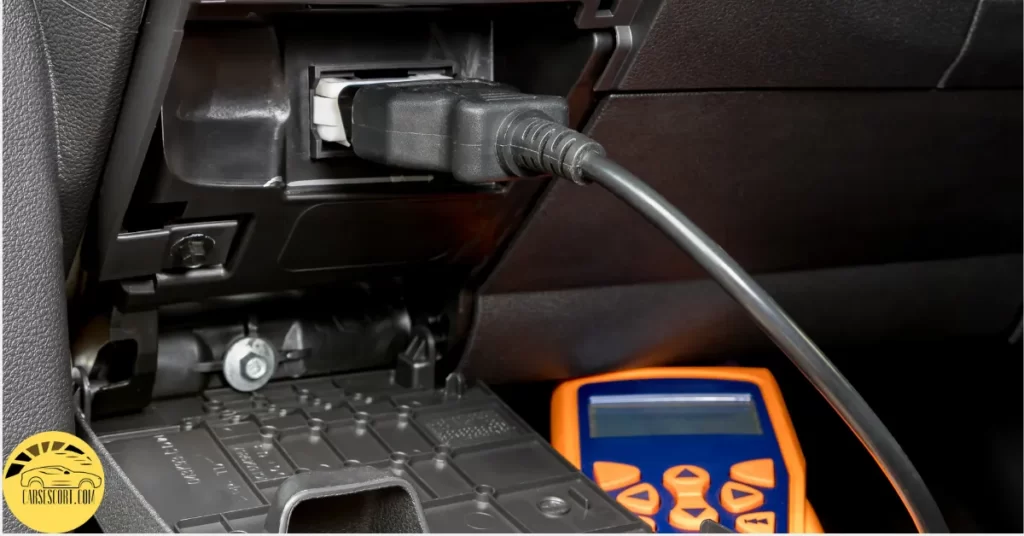
A check engine light is a severe concern for vehicles. It is recommended to have the vehicle diagnosed by a qualified mechanic or technician.
They will use specialized diagnostic tools to retrieve error codes from the OBD system, which can provide valuable information about the specific issue causing the light to illuminate.
With this information, they can accurately diagnose and repair the problem, ensuring the vehicle operates optimally and safely.

Meaning Of The Warning Colors Of The Check Engine Light
| Warning Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Red | Indicates a serious problem |
| Yellow/Orange | Needs proper attention or repaired soon |
| Green/Blue | System is operating |
How To Fix Check Engine Light Flashing Then Stops.
- Check the gas cap and Ensure that the gas cap is securely tightened, as a loose or faulty gas cap can trigger the CEL.
- Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the error codes stored in the vehicle’s ECU, which will provide clues about the specific issue.
- Check the spark plugs and ignition system and replace worn-out spark plugs or malfunctioning ignition coils that may be causing misfires.
- Inspect the oxygen (O2) sensors, as Faulty O2 sensors can affect fuel efficiency and emissions. Replace as necessary.
- Examine the mass airflow sensor (MAF). Clean or replace the MAF sensor if it is dirty or faulty, as it can affect the air-fuel mixture and performance.
- A failing catalytic converter can trigger the CEL. Check for signs of damage or clogging.
- Ensure the battery is in good condition and the alternator is charging correctly, as electrical issues can trigger the CEL.
- A malfunctioning EGR valve can affect emissions and trigger the CEL. Clean or replace if necessary.
- Examine the fuel injectors, filters, and pressure regulators for fuel delivery issues.
- Look for disconnected or damaged vacuum lines or hoses that may cause air leaks and trigger the CEL.
Why Check Engine Light Flashing And Then Stops When Accelerating?
When the check engine light flashes and then stop when accelerating, it usually indicates a misfire in the engine due to malfunctioning of the fuel delivery system. A misfire occurs when the fuel in one or more cylinders fails to ignite properly. Various issues, such as a faulty spark plug, a malfunctioning ignition coil, or a problem with the fuel system, can cause this.
When you accelerate, the engine requires more fuel and air to produce power, putting additional stress on the ignition system. If there is an existing problem with the ignition components, it can become more apparent during acceleration, leading to the CEL flashing.
FAQ
Is it safe to drive your car if the check engine light flashes and then stops?
It is not safe to drive your car in this condition. Flashing CEL typically signals a severe misfire, which can lead to further damage to the engine or other components of the vehicle. Continuing to drive the car in this state may result in a breakdown or costly repairs.
Why does the CEL flash before starting the car?
If the check engine light flashes briefly before starting your car, it is usually part of the self-diagnostic routine of the onboard computer system. During this process, the car’s computer checks various sensors and systems to ensure they function correctly. If any issues are detected, the CEL may remain illuminated or flash to indicate a specific problem.
Can bad spark plugs cause the check engine light to blink?
Yes, bad spark plugs can cause the check engine light to blink. Spark plugs are crucial in igniting the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinders. If the spark plugs are worn out or malfunctioning, they may not provide a consistent spark, leading to misfires.
When the engine misfires repeatedly, the check engine blinking light indicate a severe problem. In this case, it is essential to have the spark plugs replaced or any other necessary repairs performed.
Why is my engine light flashing and my car shaking?
If your engine light is flashing and your car is shaking, it clearly indicates a serious issue that requires immediate attention. The flashing check engine light suggests a severe misfire, which can cause the engine to shake or vibrate noticeably. Several factors can contribute to this, including ignition system problems, fuel delivery issues, or sensor failures.
Is it worse if your check engine light is flashing or solid?
A flashing check engine light is generally considered more severe than a solid one. When the check engine light is solid, it indicates a non-critical issue that needs attention but may not require immediate action. However, when the CEL is flashing, it typically signifies a severe problem, such as a misfire that can cause catalytic converter damage or other significant issues.
Affiliate Disclosure: Cars Escort is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases made through affiliate links on our site. Read Our Disclaimer .

